
In the modern digital age, cloud databases have become a cornerstone for enterprises looking to scale their applications, streamline operations, and provide flexible solutions for data management. With the growing reliance on cloud computing services, businesses increasingly shift from traditional on-premise databases to cloud database management systems.
A report from O’Reilly’s journal: An Introduction to Cloud Database, defines a managed cloud offering as one in which the vendor provides not only hardware but also the server software itself. Most vendors offer both traditional databases (such as Oracle and MySQL) and cloud-native databases that are specific to that vendor.
However, the decision to transition to a cloud DBMS (Database Management System) can be overwhelming, given the numerous available options, configurations, and performance considerations.
This blog post delves into the intricacies of cloud databases, exploring their diverse types, key considerations for selection, and insights into cloud database management. By understanding these aspects, you can make informed decisions to optimize your data management strategy in the cloud.
Want expert guidance to select the right cloud database for your business?
Understanding Cloud Databases
There is no doubt that there are ample business benefits of cloud computing. Cloud concept is a giant step in the world of technology. A cloud database is a database service that runs on a cloud computing platform. These databases are managed by a third-party provider, relieving organizations from the burden of hardware provisioning, software installation, and maintenance. Cloud databases offer several advantages over traditional on-premises databases, including:
- Scalability: Easily scale resources up or down based on demand.
- Cost-efficiency: Eliminate upfront infrastructure investments and reduce operational expenses.
- Accessibility: Access data from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Reliability: High availability and disaster recovery capabilities ensure business continuity.
Types of Cloud Databases
Cloud databases come in different forms, each designed to meet specific business needs:
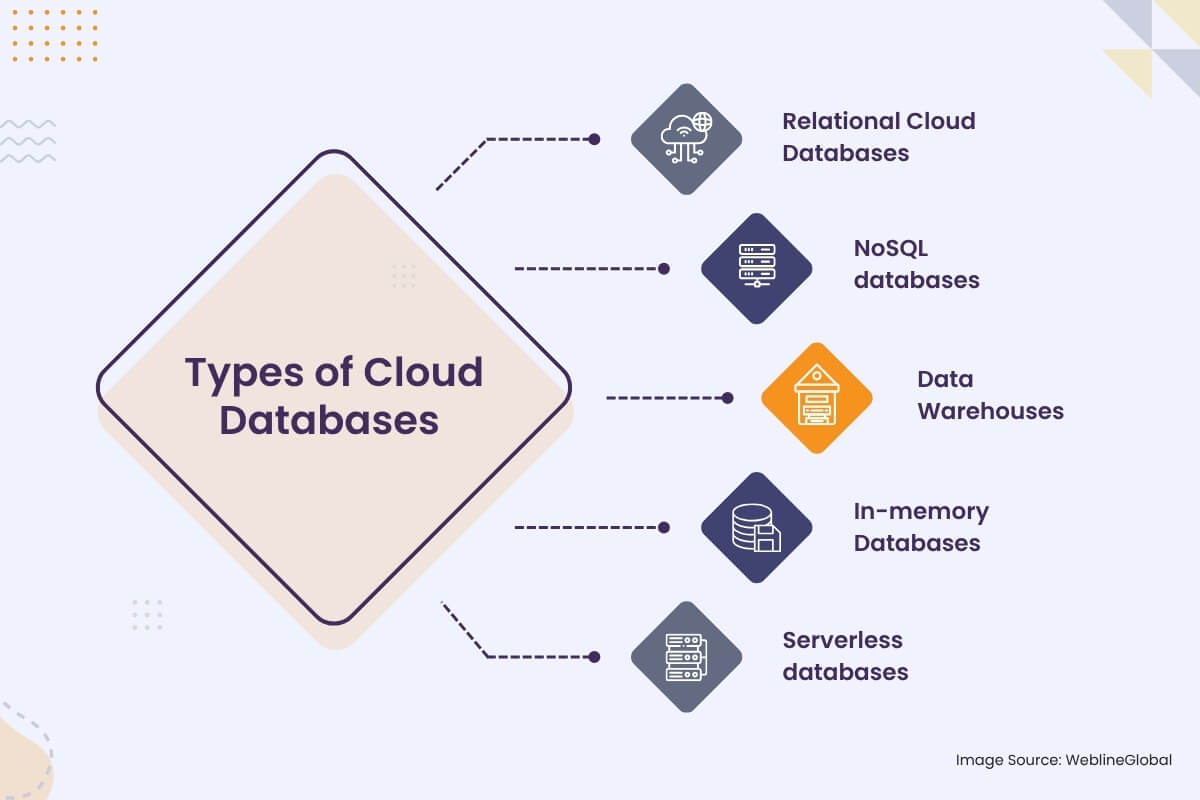
1. Relational Cloud Databases
These are traditional databases that follow the relational model. They store data in tables with fixed schemas and are optimized for transactional workloads. Examples include Amazon RDS, Microsoft Azure SQL Database, and Google Cloud SQL.
2. NoSQL databases
These databases provide a flexible schema approach, accommodating diverse data structures beyond traditional tables. They excel at handling large volumes of unstructured or semi-structured data. Common types of NoSQL databases include:
- Document databases: Store data in JSON-like documents, ideal for content management and e-commerce applications. (e.g., MongoDB, Couchbase)
- Key-value stores: Employ a simple key-value pair data model, optimized for high-speed data retrieval and caching. (e.g., Redis, Memcached)
- Graph databases: Represent data as nodes and relationships, suitable for social networks, recommendation engines, and knowledge graphs. (e.g., Neo4j, Amazon Neptune)
- Wide-column stores: Organize data into columns instead of rows, enabling efficient querying and analysis of massive datasets. (e.g., Cassandra, HBase)
3. Data Warehouses
Cloud data warehouses store large amounts of structured data for analysis and reporting. These are typically used for business intelligence and analytics tasks. Amazon Redshift and Google BigQuery are examples of cloud data warehouses.
4. In-memory Databases
These databases store data in the system’s main memory, which significantly enhances performance. They are useful for applications requiring real-time data access, such as e-commerce platforms and gaming. Examples include Redis and Amazon ElastiCache.
5. Serverless databases
These databases abstract away infrastructure management, allowing cloud developers to focus on application logic. They automatically scale resources based on workload demands and offer a pay-per-use pricing model. AWS Aurora Serverless and Google Cloud Spanner are examples of serverless databases.
Key Factors to Consider in Selecting a Cloud Database Solution
When choosing a cloud database management solution, several factors should be considered. These factors help ensure that the selected cloud DBMS aligns with the specific requirements of your application, offering both scalability and performance.
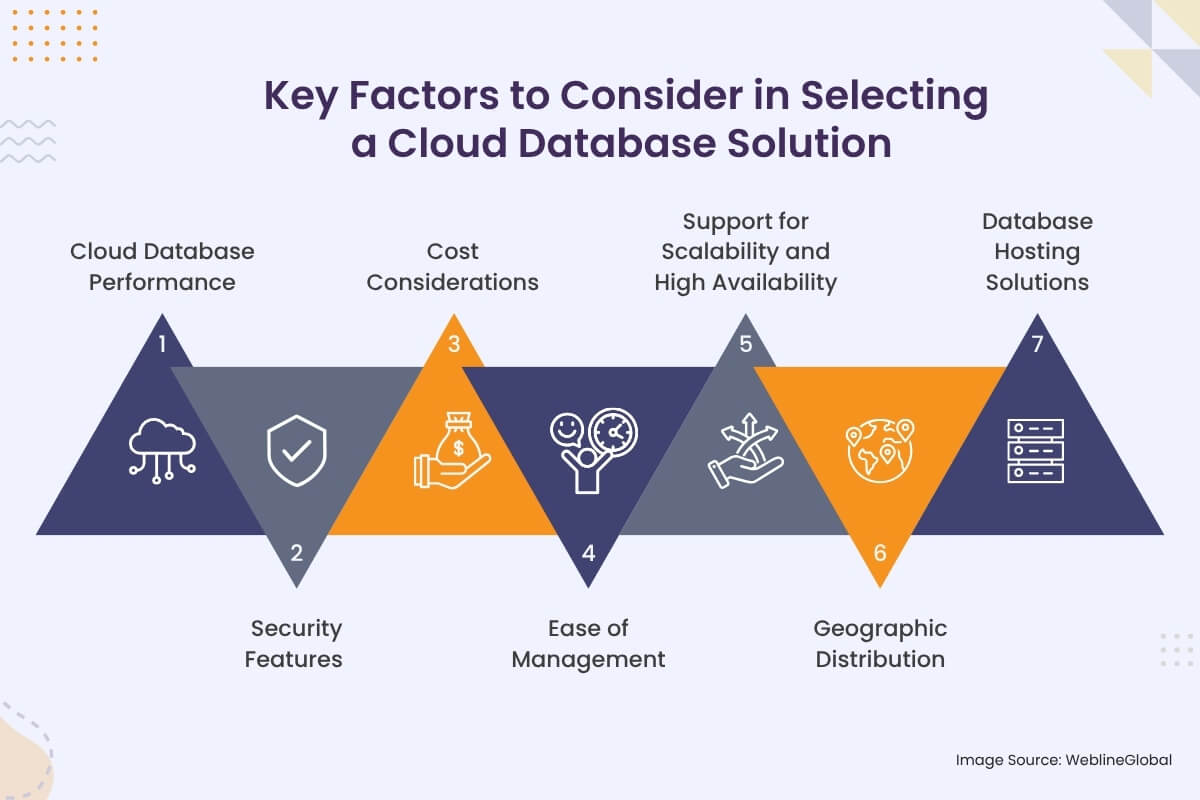
1. Cloud Database Performance
One of the most critical aspects of selecting a cloud database solution is its cloud database performance. Performance directly impacts the user experience and the overall success of your application. It’s essential to evaluate the database’s speed, scalability, and ability to handle high transaction volumes. Factors affecting performance include:
- Latency: The time taken for data to travel from the source to the destination. A low-latency solution is crucial for real-time applications.
- Throughput: The amount of data the database can process within a given time period. Applications with high data traffic, such as streaming services, require high throughput.
- Scalability: The database’s ability to grow with your application. Cloud databases that offer automatic scaling allow you to scale resources up or down as needed, ensuring your database performs optimally even during peak loads.
2. Security Features
Data security is a top priority when selecting any cloud service. The cloud database management solution must provide robust encryption, access control, and compliance features. When choosing a cloud DBMS, ensure that the provider follows industry standards and complies with data protection regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2. Key security features include:
- Data encryption (both in-transit and at-rest) to prevent unauthorized access.
- Role-based access control (RBAC) limits database access based on user roles.
- Automated backups to safeguard against data loss.
3. Cost Considerations
The cost of a cloud DBMS can vary significantly based on factors like data storage, processing power, and traffic. Some cloud database providers offer pay-as-you-go pricing, while others provide subscription-based models. It is essential to assess the total cost of ownership, including:
- Storage costs: This includes the price of storing data, both structured and unstructured.
- Compute resources: Consider how much CPU and memory your database will need to handle traffic spikes and complex queries.
- Data transfer costs: If your application requires frequent data transfer across regions, you may incur additional costs.
Comparing the cost structures of various providers will help you select the best option within your budget.
4. Ease of Management
A cloud database management system should simplify administrative tasks such as database provisioning, patching, backups, and monitoring. Choose a cloud database provider that offers an intuitive user interface, automated management tasks, and monitoring tools that give you insights into database performance, health, and security. Features like automatic backups, updates, and failure recovery can significantly reduce the management burden.
5. Support for Scalability and High Availability
A crucial advantage of cloud databases is their ability to scale seamlessly. This feature is especially valuable for businesses that experience fluctuating or unpredictable workloads. Look for cloud database solutions that offer:
- Horizontal scaling: The ability to add more instances of the database to handle increased demand.
- Vertical scaling: The ability to increase the resources (CPU, RAM, storage) of a single instance.
- High availability: Ensure that your database can tolerate failures and continue to operate without disruption, typically through multi-region replication or automatic failover mechanisms.
6. Geographic Distribution
Geographic distribution plays a vital role in the performance and reliability of a cloud database. The ability to replicate and distribute data across multiple regions is essential for minimizing latency, improving user experience, and ensuring high availability. Key factors to consider include:
- Data replication: Storing copies of data in various locations to ensure reliability and reduce the risk of data loss.
- Reduced latency: Hosting data closer to users in different regions helps decrease response times, providing a faster experience for global users.
- Fault tolerance: Distributing data across multiple regions ensures that if one region experiences an outage, the database can still function seamlessly by failing over to another region.
- Compliance with local regulations: Some jurisdictions require data to be stored within specific regions, making geographic distribution crucial for compliance.
7. Database Hosting Solutions
When selecting a cloud database management system, the type of hosting solution is crucial for meeting performance, scalability, and budget requirements. Various options are available, each with unique benefits:
- Managed databases: These are fully managed solutions where the cloud provider handles database setup, maintenance, backups, and updates. Ideal for businesses seeking a hands-off approach.
- Marketplace apps: Cloud providers offer marketplace applications that allow users to quickly deploy pre-configured databases. These are often flexible and easy to integrate with other cloud services.
- Database clusters: Suitable for applications with high availability and scalability needs, database clusters distribute the load across multiple servers, ensuring redundancy and improved performance.
- Custom deployments: Organizations with specific requirements may choose to deploy their own database on cloud infrastructure, providing more control but requiring more management.
Streamline your operations with scalable, secure cloud database solutions tailored to your needs.
Cloud Database Performance: An Essential Consideration
To understand the full impact of cloud database performance, it is essential to recognize the potential bottlenecks that could hinder your application. Performance can be influenced by the following factors:
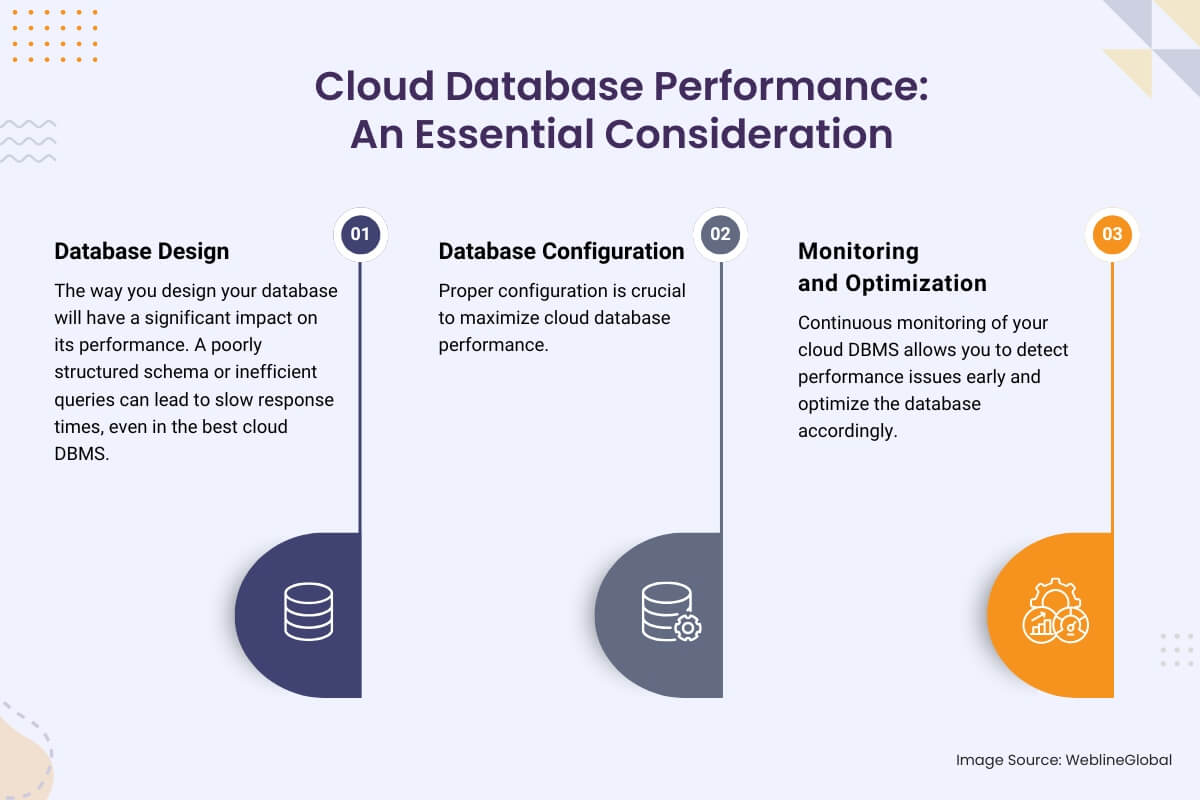
1. Database Design
The way you design your database will have a significant impact on its performance. A poorly structured schema or inefficient queries can lead to slow response times, even in the best cloud DBMS. Focus on:
- Normalization: Minimize redundancy in data to optimize storage.
- Indexing: Proper indexing ensures faster data retrieval and query performance.
- Query optimization: Write optimized queries that reduce resource consumption and improve response time.
2. Database Configuration
Proper configuration is crucial to maximize cloud database performance. This includes:
- Resource allocation: Ensuring the right amount of CPU, RAM, and storage for your workload.
- Connection pooling: Reducing the overhead of establishing new database connections by reusing existing ones.
- Caching: Implement caching mechanisms to reduce database load by storing frequently accessed data in memory.
3. Monitoring and Optimization
Continuous monitoring of your cloud DBMS allows you to detect performance issues early and optimize the database accordingly. Tools like Amazon CloudWatch, Google Stackdriver, and Azure Monitor provide comprehensive insights into the health and performance of your cloud database. Regular performance audits help identify areas of improvement, ensuring your database performs optimally.
Cloud Database Management
Effective cloud database management is crucial for ensuring optimal cloud database performance, security, and cost-efficiency. Key aspects of cloud database management include:
- Monitoring: Track key metrics such as resource utilization, query performance, and availability to identify potential issues.
- Performance optimization: Fine-tune database configurations, optimize queries, and implement caching strategies to enhance cloud database performance.
- Security management: Implement access controls, encryption, and auditing to safeguard sensitive data.
- Cost optimization: Utilize resource scaling, reserved instances, and pricing models to minimize cloud database expenses.
- Backup and recovery: Establish regular backups and disaster recovery plans to ensure business continuity.
Cloud DBMS Features and Benefits
A cloud DBMS (Database Management System) provides the software infrastructure for managing and interacting with cloud databases. It offers a range of features that simplify cloud database management and enhance operational efficiency. Some key features and benefits of a cloud DBMS include:
- Automated provisioning: Streamlined database deployment and configuration.
- Scalability and elasticity: Dynamically adjust resources based on workload demands.
- High availability and fault tolerance: Ensure continuous operation even in the case of infrastructure failures.
- Data security and compliance: Robust security measures to protect data integrity and confidentiality.
- Simplified management: Intuitive interfaces and tools for managing database operations.
Best Practices for Cloud Database Performance
Optimizing cloud database performance is essential for ensuring application responsiveness and user satisfaction. Some best practices for maximizing cloud database performance include:
- Choose the right database type: Select a cloud database that aligns with your workload characteristics and data model.
- Optimize data modeling: Design efficient database schemas and data structures.
- Use appropriate indexing: Create indexes on frequently accessed columns to speed up query processing.
- Optimize queries: Write efficient queries that minimize data retrieval and processing.
- Implement caching: Utilize caching mechanisms to store frequently accessed data in memory for faster retrieval.
- Monitor and analyze performance: Regularly track cloud database performance metrics to identify and address bottlenecks.
Conclusion
Selecting the optimal cloud database solution for your application involves a careful assessment of your requirements, performance needs, security considerations, and cost constraints. It is crucial to choose a cloud DBMS that not only meets your immediate requirements but can also scale with your business growth.
Prioritize factors like cloud database performance, security, scalability, and ease of management when evaluating your options. The right choice will provide a reliable, cost-effective solution that enhances your application’s performance, reduces administrative overhead, and supports your long-term goals.
WeblineGlobal can help you with quality cloud technology services to help you choose a cloud database management system to streamline your operations and provide the foundation needed to support data-intensive applications. Our consultants can help you analyze the available solutions by understanding your specific requirements to make an informed decision that will lead to enhanced productivity and your business’s growth.
Social Hashtags
#CloudDatabases #CloudSolutions #DatabaseManagement #DigitalTransformation #AppDevelopment #DataManagement #TechInnovation #BusinessGrowth #WeblineGlobal
Ready to optimize your applications with the best cloud database solution?




